How does Primary dentition appear?
[mme_highlight]The first tooth to appear is the central incisor, between 6 and 12 months. The most common clinical manifestations of teething in children are fever, drooling and diarrhea. Clean and healthy teeth are not only important to chew the food properly but also to pronounce the words clearly.[mme_highlight]
Humans are diphyodont, which means we have 2 sets of teeth in our lifetime- a temporary set, with 20 teeth (also known as primary, baby, milk or lacteal dentition) and a permanent dentition composed by 32 teeth. Diphyodont literally means “two generations of teeth”. The chart below can help to understand the eruption and shedding pattern of the teeth in children.
[mme_databox]
Eruption and Shedding pattern of primary teeth
| Erupts at | Sheds at | |
|---|---|---|
| Central incisor | 6-12 mo | 6-7 y |
| Lateral incisor | 9-16 mo | 7-8y |
| Cuspid or Canine | 16-23 mo | 9-12 y |
| First bicuspid | 13-19 mo | 9-11 y |
| Second Bicuspid | 23-31 mo | 10-12 y |
mo- months and y-years
[/mme_databox]
Primary Teeth: Those beautiful pearls
When the child is born, there is an immediate reflex to suck. Breast milk provides all the essential nutrients and water for the first 6 months. Babies start basic food after 6 months, when the first tooth forms (chart1). Dentition begins in fetus at 4 months and at the time of birth the crown of the first 20 deciduous teeth is formed. Between 2 1/2 and 3 years, the baby has 20 white teeth to flaunt. The process of dentition is dynamic – there is continuous growth of the child’s jaw that makes way for the permanent teeth.
How to take care of primary teeth?
Primary teeth though deciduous, need proper care. Clean and healthy teeth are not only important to chew the food properly but also to pronounce the words clearly. Infectious gums lead to oral pain and compromise the healthy growth of permanent teeth. In children, tooth decay is called early childhood caries, baby bottle tooth decay or nursing mouth syndrome.
How does teething affect children?
Teething is often remembered by most parents as a phase of distress and discomfort. The child is disturbed with the simultaneous changes in the oral cavity. Ballooning of the gums, with swelling and redness, as well as oral ulcers and increased drooling are some of the problems encountered by children. Redness of mucosa is a very common phenomenon and occurs in 30-90% of the babies.
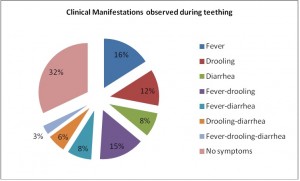
Noor-Mohammed and Basha in a recent study (2012) showed that the most common clinical manifestations of teething in children are fever, drooling and diarrhea (Chart2). These manifestations were prominent during the eruption of primary incisors. Boys tend to suffer from diarrhea more than girls, though other clinical manifestations did not vary much with gender.
[mme_databox]
Clinical Manifestations observed during teething
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012 May 1;17 (3):e491-4.
[/mme_databox]
How can parents help to relief teething associated symptoms?
- Something to chew on: Give the child something to chew, like a cold washcloth.
- If the child is old enough to eat, give her/him something cold to eat such as yogurt, ice-cream or an apple purée. Cold numbs the gums and it is often regarded as a natural anesthetic.
- Unsweetened teething crackers are available in the market and are believed to provide relief to the child.
- Rubbing the sore gums with clean fingers or topical relief gels can also help, though you should refer to your doctor first.
- Drooling often causes a rash on the baby’s face. In such a situation, just wipe the face with a soft cloth. Applying petroleum jelly on the chin also brings relief.
Can my baby have Dental Caries?
Dental caries occur at an early age in children; in fact, caries can appear as soon as there is an eruption of the first tooth, and is presented as white lines or spots. It is a chronic disease in which teeth have bacteria (a mutant of streptococci). These bacteria are fed by sugars (monosaccharide and disaccharides) producing acids which erode teeth causing infection.
[mme_databox]
- Only 6% of the chewing career of an average human being (70 years) uses deciduous dentition
- Timing of eruption of teeth is governed by genetics
- Shedding of deciduous teeth begins early in girls
[/mme_databox]
Summary and Recommendations
- The first tooth to appear is the central incisor, between 6 and 12 months.
- Teething can be a source of distress both for children and parents. According to a study, the most common clinical manifestations of teething in children are fever, drooling and diarrhea.
- Hygiene and general good care of teeth are essential to help chewing, speaking and a normal growth of permanent teeth.
Oral care tips for infants – Do’s:
- Wipe your child’s gums after each feed
- Brush your child’s teeth and supervise them if fluoride toothpaste is used. They must be taught the concept of rinsing the teeth after brushing
Oral care tips for infants – Don’ts:
- Never let your baby sleep with sweetened juice of milk-bottle in the mouth
- Never dip pacifier in honey or sugar syrup
[mme_references]
References
- Tooth eruption. The primary teeth. JADA, Vol. 136, 2005.
- Hulland SA, Wake MA. Eruption of the primary dentition in human infants: a prospective descriptive study. Pediatric Dentistry – 22:5, 2000.
- Noor-Mohammed R, Basha S. Teething disturbances; prevalence of ob- . Teething disturbances; prevalence of ob- Teething disturbances; prevalence of objective manifestations in children under age 4 months to 36 months. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal.;17 (3):e491-4, 2012 May 1.
- Douglass JM, Douglass AB, Silk HJ.A practical Guide to Infant Oral Health. Am Fam Physician. 2004 Dec 1;70(11):2113-2120.
[/mme_references]